The Role of Page Speed in SEO: How to Improve Your Website’s Performance
By Brendan Byrne Tuesday, March 4, 2025

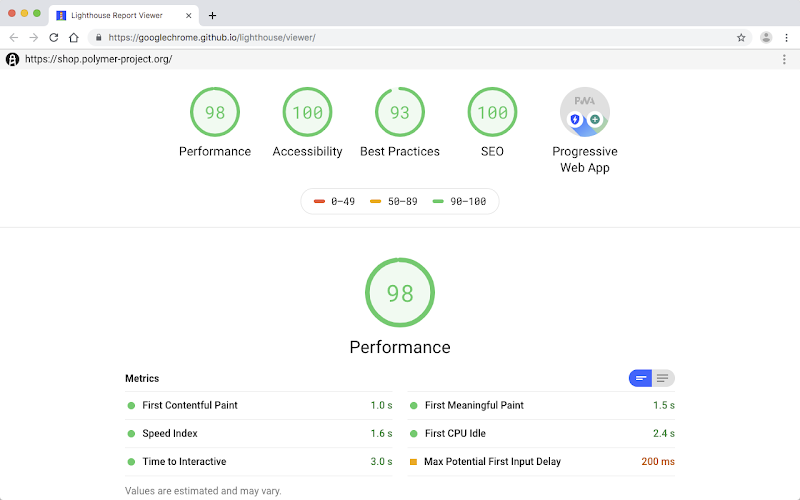
Page speed has become a critical factor for both user experience and search engine optimisation (SEO). Users expect webpages to load quickly; delays can lead to frustration, high bounce rates, and lost conversions. Moreover, search engines like Google use page speed as a ranking factor, making it essential for businesses aiming to enhance their online visibility. This article explores the importance of page speed, effective tools for testing it, optimisation techniques, and its impact on search rankings, specifically catering to web developers, business owners, and digital marketers.
Importance of Page Speed for SEO and User Experience
Page speed is the time taken for a webpage to fully load in a user’s browser. Research indicates that users expect a webpage to load in two seconds or less, and if it takes longer, they are likely to abandon the site. According to Google, 53%25 of mobile users leave a site that takes over three seconds to load.
From an SEO perspective, page speed is a significant ranking factor. Faster websites not only provide a better user experience but also lower bounce rates, increase dwell time, and ultimately lead to higher conversion rates. Google’s algorithm rewards websites that offer a seamless user experience, making page speed a crucial element for improving search rankings.
Key Metrics to Monitor
When assessing page speed, several key metrics can help determine your site's performance:
- First Contentful Paint (FCP): This metric measures the time it takes for the first piece of content to appear on the screen.
- Time to Interactive (TTI): TTI indicates how long it takes for the page to become fully interactive for users.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): This metric focuses on the loading performance of the largest visible content element in the viewport.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): CLS measures visual stability, quantifying how much content shifts as the page loads.
Key Tools to Test Website Speed
A variety of tools are available to test and assess website speed. Here are some of the most effective ones:
1. Google PageSpeed Insights
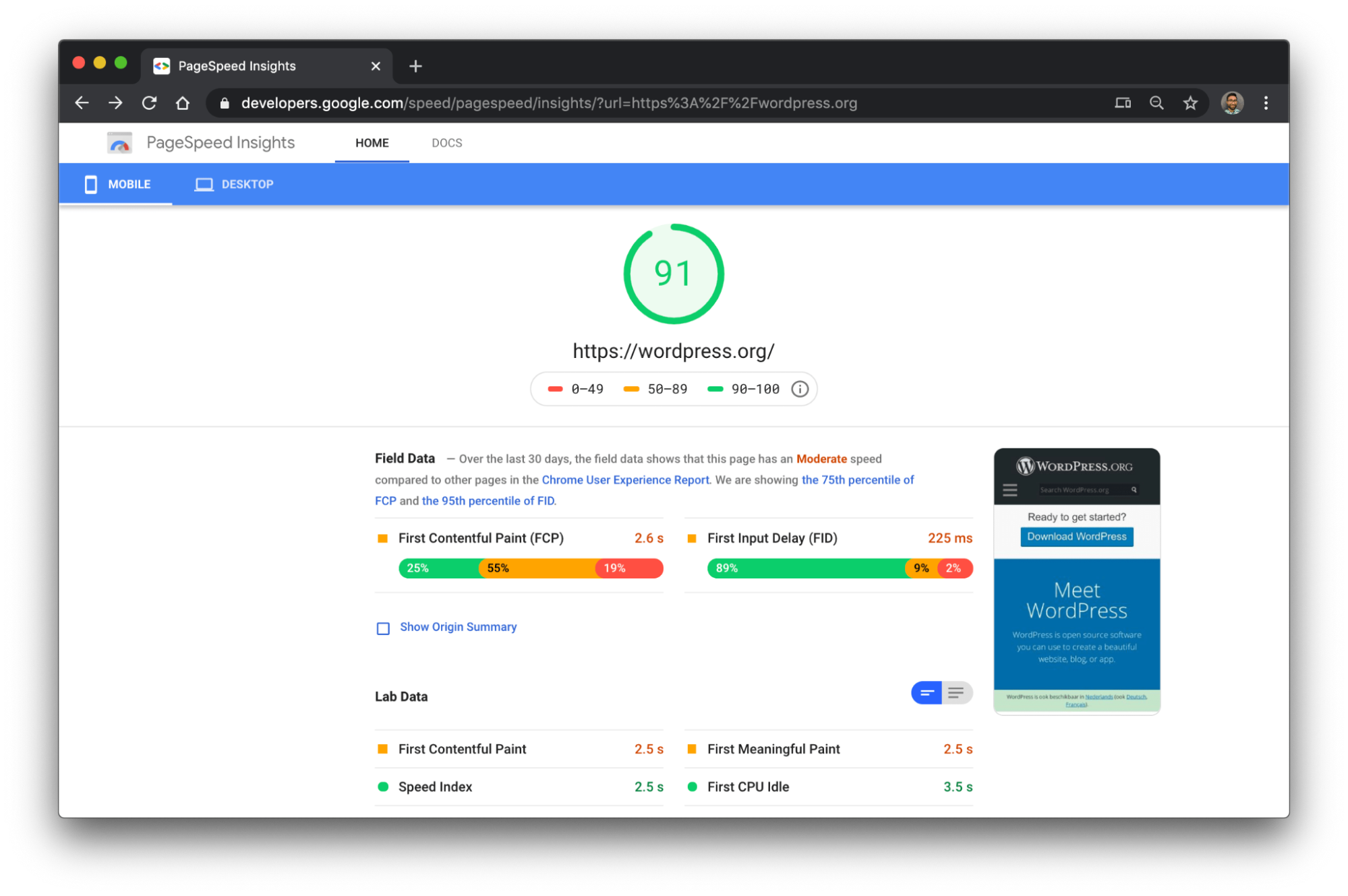
Google PageSpeed Insights is a widely-used tool that evaluates the performance of a webpage on both mobile and desktop devices. It provides a score out of 100, along with suggestions for improvement. The tool highlights various performance metrics and offers actionable insights tailored to specific issues affecting your site.
2. Google Lighthouse
Google Lighthouse is an open-source tool that aids developers with web performance, accessibility, and SEO audits. It can be run from Chrome DevTools, the command line, or as a Node module. Lighthouse provides a comprehensive overview of performance metrics and offers recommendations to enhance page speed.
3. GTmetrix
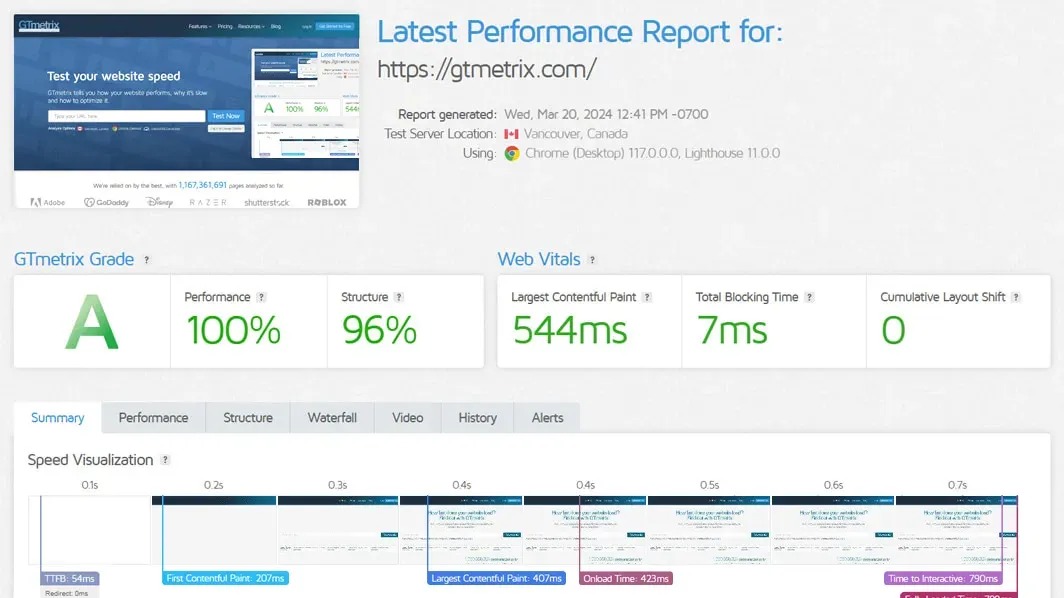
GTmetrix combines Google PageSpeed Insights and YSlow metrics to provide a thorough analysis of webpage performance. It allows users to test their site’s speed from different locations and offers a detailed report on various performance indicators.
4. WebPageTest
WebPageTest is another powerful tool that allows users to test their website speed from multiple locations worldwide. It offers advanced features, such as filmstrip view and visual comparisons of different performance metrics.
Techniques to Optimise Images, Scripts, and Caching
1. Image Optimisation
Images often contribute significantly to page load times. Here are several strategies for optimising images:
- Compress Images: Use tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim to compress images without sacrificing quality. This reduces file sizes and enhances loading times.
- Use Appropriate Formats: Choose the right image formats; for instance, use JPEG for photographs, PNG for graphics with transparent backgrounds, and SVG for logos and icons.
- Implement Responsive Images: Use the srcset attribute in the
tag to serve different image sizes based on the user’s device, ensuring optimal loading for both desktop and mobile users.
2. Script Optimisation
JavaScript and CSS files can bloat your website, causing delays in rendering. Here are optimisation techniques to consider:
- Minification: Minify JavaScript and CSS files by removing unnecessary characters, comments, and whitespace. Tools like UglifyJS and CSSNano can help achieve this.
- Asynchronous Loading: Load JavaScript files asynchronously to prevent them from blocking the rendering of the page. This ensures content is displayed quickly while scripts load in the background.
- Defer Unused Scripts: Identify and eliminate any scripts that are not essential to the initial loading of the page.
3. Caching Strategies
Implementing effective caching strategies can significantly improve page speed. Here are some approaches to consider:
- Browser Caching: Set expiry dates or a maximum age for certain types of content, so returning visitors don’t have to download the same files again.
- Server-Side Caching: Use tools like Varnish or Redis to cache dynamic content on the server, reducing load times for repeat visitors.
- Content Delivery Network (CDN): Employ a CDN to store cached versions of your website across various locations. This reduces the distance between the user and the server, improving loading times.
Mobile vs. Desktop Performance
While page speed is crucial for both mobile and desktop users, their experiences can differ significantly. Mobile devices often face additional challenges, such as varying connection speeds and device capabilities.
Mobile Optimisation
Google prioritises mobile-first indexing, meaning the mobile version of your site is considered the primary version for ranking purposes. To optimise for mobile users:
- Implement Responsive Design: Ensure your website is fully responsive and adapts to different screen sizes, improving user experience across devices.
- Avoid Intrusive Pop-Ups: Limit the use of intrusive pop-ups that can disrupt the user experience on mobile devices.
- Optimise for Touch: Ensure buttons and links are appropriately sized for touch interactions, enhancing usability on mobile devices.
Case Studies: How Improved Speed Leads to Higher Rankings
Case Study 1: eCommerce Website
An eCommerce website improved its page load time from 5 seconds to 2 seconds by optimising images and implementing a CDN. As a result, the site saw a 25% increase in conversion rates and a significant improvement in organic search rankings, moving from the second page of Google to the first.
Case Study 2: Local Business
A local service provider focused on optimising their website's speed by minifying CSS and JavaScript files. The site’s loading time reduced from 4 seconds to under 2 seconds, resulting in a 40% increase in traffic and improved visibility on Google Maps.
Page speed is more than just a technical metric; it’s a cornerstone of a successful online presence. A fast-loading website not only enhances user satisfaction but also strengthens your search engine rankings, helping you stay ahead of the competition. By understanding the impact of page speed on SEO and user experience, utilising the right tools, and applying proven optimisation techniques, you can create a website that performs seamlessly across devices.
In today’s fast-paced digital environment, slow-loading websites simply cannot compete. Prioritising page speed isn’t just about compliance with search engine algorithms—it’s about delivering value to your users and maximising your business potential. Take action today to optimise your site’s performance and enjoy the benefits of improved traffic, higher conversions, and long-term success.